Whether you are running cold outreach, nurturing leads, or sending out transactional updates, bounced emails are an annoyance—and more than that, they signal that something is wrong.
At Warmy.io, we’ve been running controlled deliverability experiments across major email service providers (ESPs)—Gmail, Outlook/MS365, Yahoo, AOL, and Zoho—to understand exactly why emails bounce, what those bounce codes actually mean, and how to fix the underlying issues.
This blog post focuses on hard vs. soft bounce root causes, real-world thresholds, and remediation strategies you can actually use—especially if you’re battling rejections, spam folder traps, or silent greylisting.
Bounce basics: hard vs. soft bounces
Before diving into provider-specific insights, it’s important to understand the two core types of email bounces:
Hard-bounce:
❌ Invalid addresses
❌ Spam or email rejection
❌ DMARC failure
Soft Bounces:
✅ Full mailbox
✅ Greylisting
✅ Temporary server issue
What are hard bounces?
These are permanent failures which come with a 5xx error message. Your email is rejected and won’t be retried. Common causes include:
- Nonexistent email addresses (e.g., typos or abandoned inboxes)
- Failing SPF, DKIM, or DMARC checks
- IP/domain blacklisting
- Content flagged as spam or violating ISP policy
Related Reading: Fixing 550 Permanent Failure for One or More Recipients: A Complete Guide
What are soft bounces?
These are temporary issues with 4xx codes. Your email didn’t go through, but the server may try again. Common causes include:
- Greylisting (a spam control tactic that delays unknown senders)
- Recipient’s mailbox is full
- Server is busy or temporarily unavailable
- Volume-based throttling or rate limits
Soft bounces are often an early warning. If ignored, they can snowball into permanent failures. A smart sender watches for these signs and adapts fast. This distinction is key to understanding how each ESP reacts to your emails—and what signals they send when something goes wrong.
A bird’s eye view of common hard and soft bounces per ESP
Here is a comprehensive overview of common hard and soft bounce scenarios across the most widely used email service providers (ESPs): Gmail, Outlook/MS365, Yahoo/AOL, and Zoho.
Though every Email Service Provider (ESP) and Internet Service Provider (ISP) have unique bounce codes and policies, they still usually follow the 4xx = soft, 5xx = hard naming conventions.

While this table highlights key bounce codes and common causes, the Warmy Research Team also took a deep dive into each ESP.
Gmail: Navigating bounces with precision
Gmail, one of the most popular email platforms, offers detailed bounce messages that can help you pinpoint the exact reason for a delivery failure.
Hard bounce causes on Gmail
When Gmail returns a hard bounce, it means your email will not be delivered, and you need to take action immediately. Common hard bounce causes include:
Invalid recipient addresses (550 5.1.1)
If you receive this bounce, the recipient’s email address is invalid or perhaps no longer active. Read also: SMTP Error 550 5.1.1 – How to Resolve [SOLVED]
Spam rejections (550 5.7.1)
Gmail will block any message that appears to be spam, whether that is because it does not trust the sender or the content has been flagged. There may also be blacklisting or previous suspicious email coming from your sending IP or domain, causing this kind of bounce. Read also: SMTP Error 550 5.7.1 – How to Resolve [SOLVED]
Authentication failures (550 5.7.26)
This happens when you don’t have the proper authentication records set up, or when your email doesn’t meet Gmail’s strict security requirements.
Q: What are proper authentication records and how do they impact bounces?
A: Proper authentication records include SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). These records confirm that emails are being sent from real senders and prevent spoofing and phishing attempts.
🔖 Related Reading: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Boosting Email Security and Deliverability
Message size or other policy blocks (552 5.3.4)
Note: Gmail allows you to attach up to 25MB to a single email. If you exceed the limit or violate Gmail’s other content policies, your email can be permanently rejected. Read also: SMTP Error 552 5.3.4 – How to Resolve [SOLVED]
Soft bounce causes on Gmail
While soft bounces indicate temporary issues that may resolve on their own, they shouldn’t be ignored or underestimated.
Greylisting (421 4.7.0)
If Gmail detects a high volume of unsolicited email from your IP, it may temporarily block the message, asking you to retry. The mail server will usually retry and deliver the message after some time. Read also: SMTP Error 421 4.7.0 – Temporary Email Rejection: Causes & Fixes
Mailbox full (452 4.2.2)
If the recipient’s inbox is full then Gmail doesn’t deliver the email and returns a soft bounce with a 452 error. This implies that the mailbox is full already, and can’t have any more messages added to it until the user makes room. Read also: SMTP Email Error 452 4.2.2 – How to Resolve [SOLVED]
Temporary authentication failures (421 4.7.0)
If there’s an issue with your email’s authentication information (like SPF or DKIM), Gmail might temporarily defer the email. This soft bounce typically resolves after retrying once the authentication issue is addressed.
Outlook / Hotmail / MS365: Mastering the art of deliverability
Outlook and MS365 (Microsoft) are essential players in the world of email communication, especially in business settings.
Hard bounce causes on Outlook/MS365
Some of these hard bounces on Outlook/MS365 are similar to how Gmail sends their error messages. Here are the most common causes:
User or mailbox not found (550 5.1.1)
This happens usually when the receiver has an invalid email address, or does not exist. This may be the result of a typo in the recipient’s email address, or that the recipient’s account no longer exists. Likewise, if the sender uses too many unknown recipients, this will also trigger a block.
Policy blocks – Spam content or reputation issues (550 SC-001, 550 OU-002)
Outlook/MS365 uses various spam filters that reject emails with content deemed suspicious or from senders with a poor reputation.
Q: What are spam filters?
A: Spam filters are mechanisms that are used by email services to eliminate unsolicited or dubious email based on specific conditions like content, reputation of the sender, and recipient behaviors.
🔖 Related Reading: Spam filters: everything you need to know
IP address blocked or blacklisted (550 SC-004, 550 OU-001)
If your sending IP or domain has been flagged for spam or excessive complaints, Outlook/MS365 may hard bounce your emails. You might encounter codes like 550 SC-004 or 550 OU-001, indicating your IP is blacklisted. Read also: Email Domain & IP Blacklist Removal: 5 Steps to Delist
Authentication failures (Sender ID/SPF Issues – 550 5.7.1)
If your email fails Microsoft’s Sender ID checks or other authentication methods, you will receive a hard bounce like 550 5.7.1, indicating that the email was rejected due to failed SPF/DKIM checks.
Prohibited sender sources
In an effort to protect its users, Outlook refuses emails from certain IPs. For example, if you’re sending from a residential or dynamic IP address Microsoft will hard-bounce it.
Soft bounce causes on Outlook/MS365
Soft bounces are temporary issues that may resolve on their own after retrying the email. Here are the most common soft bounce causes:
Rate limiting & throttling (421 RP-001, RP-002, RP-003)
Outlook/MS365 applies rate limits to control high-volume sending and to prevent abuse. If you exceed the allowable sending rate, you’ll get a 421 RP error code.
Temporary server or network issues (451 4.7.500)
If Outlook/MS365 is temporarily unavailable or facing server congestion, you may encounter a 451 4.7.500 error, indicating a temporary failure. This can happen during periods of high load or network issues.
Spam filter deferrals (421 4.7.0)
If Outlook/MS365 detects suspicious content or behaviors in your email, it may initially defer the message. This is a signal to adjust your sending behavior such as reducing spam-like content and improving sender reputation.
Deferred due to open relay or bounce backlog (451 4.7.1)
Sometimes, Outlook/MS365 may temporarily defer emails if your sending behavior is similar to an open relay or if there is a backlog of bounces. This is a soft bounce and can often be resolved by improving list hygiene and reducing invalid recipients.
Yahoo Mail: Tackling the bounces and enhancing deliverability
Yahoo Mail, though less dominant in the global email landscape than Gmail or Outlook, is still a major player, especially in the United States and for certain business users.
Hard bounce causes on Yahoo
Invalid recipient address (554 5.1.1)
If an email is sent to a non-existent or misspelled Yahoo address, it will trigger a hard bounce with the error code 554 5.1.1, indicating the recipient doesn’t have a Yahoo account.
Policy rejections (554 5.7.9, 554 Message not allowed)
Error codes like 554 5.7.9 indicate that Yahoo has blocked your message due to content that’s been flagged as spam or due to a poor sender reputation.
Authentication failures (DMARC/ DKIM Issues – 521 5.2.1)
Yahoo enforces strict DMARC and DKIM policies, rejecting any email that doesn’t align with the domain’s authentication settings.
Blocked IP or blacklisted address (553 5.7.1 [BLXX])
Yahoo utilizes external blacklists like Spamhaus, and if your IP address or domain is listed, it will reject the email outright. 🔖 Related Reading: Remove IP from Yahoo Blacklist: The Ultimate Fix [SOLVED]
Soft bounce causes on Yahoo Mail
Soft bounces are temporary failures that may resolve after retrying the email. Common soft bounce causes for Yahoo include:
Greylisting (421 4.7.0 [TS01], [TS02])
Yahoo employs greylisting for new senders or those with a low reputation. If you retry after a short delay, Yahoo typically accepts future emails from your server once it’s deemed legitimate.
Mailbox full (452 or 552 error codes)
If the mailbox on a recipient’s mail server is full, Yahoo will generate a soft bounce, meaning the message will not be delivered until the recipient makes room. You can try sending the mail when the mailbox is empty. You may also want to take the time of writing to suppress the address.
Temporary server or network issues (451 4.7.0)
Yahoo can sometimes face server or routing issues that prevent delivery. In these cases, a 451 4.7.0 error indicates that the server is temporarily unavailable, and retrying later often resolves the issue.
Suspicious traffic or high volume (421 4.7.0 [TS03])
If Yahoo detects unusual sending patterns or a high volume of emails from your server, it may temporarily defer delivery with error codes like 421 [TS03]. This is often due to a high complaint rate or sudden traffic spikes, which might be perceived as spammy behavior.
AOL Mail: Overcoming bounce barriers
Although AOL Mail is not as widely used as Gmail or Outlook, it still holds a strong user base.
Hard bounce causes on AOL Mail
Non-existent address (521 5.2.1)
This error occurs when the account does not exist or has been disabled. This is a permanent failure, and the invalid address should be removed from your mailing list.
DMARC failures (521 5.2.1)
AOL maintains tight DMARC policies, and if your email doesn’t pass DMARC authentication (e.g., doesn’t align with the sender’s DMARC policy), it will result in a hard bounce.
IP address blocked or blacklisted (554 5.7.1)
In the event that AOL has determined that the sending IP is included in the internal blacklist, or that the IP was flagged as a result of spam-like behavior, it will return a hard bounce.
Soft bounce causes on AOL Mail
Soft bounces are temporary failures, and emails might still be delivered if attempted later. Common soft bounce causes for AOL include:
Greylisting (421 4.7.0 [TS01], [TS02])
AOL uses greylisting to temporarily reject emails from unknown senders, particularly those with new IPs or domains. If you encounter a 421 4.7.0 or [TS01] deferral, it means AOL is delaying delivery to see if the sender retries, which is a normal practice.
Full mailbox (452 or 552)
These codes indicate that the recipient cannot receive the email because their mailbox has exceeded its storage quota. The bounce is temporary, and the message will likely be delivered once the recipient clears space.
Temporary server or routing Issues (451 4.7.0)
Periodically, AOL may encounter server and routing issues that will result in a temporary failure of the delivery. In these cases, a 451 4.7.0 error code indicates that the email could not be delivered at the time, but retrying later may resolve the issue.
Suspicious content or high volume (421 4.7.0 [TS03])
High volume or rapid increases in sending activity can trigger a 421 deferral, indicating that AOL’s filters are flagging the email for review. It’s important to scale your sending gradually to avoid these issues.
Zoho Mail: Smaller but still strict
Zoho Mail is a great choice for businesses, particularly those utilizing Zoho’s CRM suite, and knowing its bounce causes and mitigation is important for keeping your email campaigns running smoothly.
Hard bounce causes on Zoho Mail
Hard bounces are permanent delivery failures, and they can occur for the following reasons on Zoho Mail:
Non-existent Address (550 5.1.1)
As with most ESPs, sending to an invalid or non-existent address results in a hard bounce. This bounce indicates that the recipient’s email address does not exist in Zoho’s system.
Spam content rejection (554 5.7.1)
Zoho has strict spam filters and may block emails that are flagged as spam. Common reasons include sending from a blacklisted IP, having suspicious links, or poor reputation.
Failed IP reputation or blacklist (550 5.7.1)
If your sending IP is listed on a blacklist (like Spamhaus or SpamCop), Zoho will reject the message. This rejection is due to the IP’s bad reputation, often caused by spam complaints or hitting spam traps.
Attachment or virus policy violation (552 5.2.0)
Zoho may block emails containing attachments that are deemed suspicious, such as viruses or disallowed file types. This bounce is permanent until the issue with the attachment is resolved.
Soft bounce causes on Zoho Mail
Soft bounces are temporary failures and may be resolved after retrying. Common causes of soft bounces for Zoho include:
Greylisting (451 4.7.1)
If your IP or domain has never sent to Zoho before, your email may initially be deferred, indicating that Zoho is temporarily rejecting the message to assess the sender. After retrying, Zoho usually accepts the email.
Full mailbox (450 4.2.2 or 552)
If the recipient’s mailbox is full, Zoho will issue a soft bounce to indicate that the mailbox cannot accept the email due to lack of space. The email will be retried later, and delivery is usually successful once the recipient clears space.
Temporary system or DNS Errors (421 4.3.0)
Occasionally, Zoho may encounter transient issues such as server downtime or DNS resolution problems, causing a 421 4.3.0 soft bounce. These errors are temporary, and the message will likely be delivered once the system stabilizes.
Anti-spam threshold deferral (421 4.7.1)
Zoho may temporarily defer delivery if your sending behavior triggers suspicion, such as a burst of emails that appear spammy. This deferral is often accompanied by an error code, indicating that the message is temporarily held for review. You can resume sending once the issue is addressed.
How to reduce bounce rates per ESP
Reducing bounce rates is essential for maintaining high email deliverability across all major ESPs. Different providers have varying policies, thresholds, and filtering systems that can affect how your emails are treated.
Understanding the nuances of each ESP and applying specific mitigation strategies will help you significantly reduce bounce rates and ensure better inbox placement. Below is a summary table outlining actionable steps you can take to reduce bounce rates for each ESP based on the information we discussed in earlier sections.

You will notice that the mitigation and optimization strategies per ESP all have something to do with implementing good sending practices. Regular monitoring of domain reputation, careful warm-up practices, and proper authentication setups will significantly reduce bounce rates and improve inbox placement.
How Warmy.io can help mitigate bounce rates
Email deliverability is a critical aspect of any email marketing strategy, and mitigating bounce rates is one of the most effective ways to ensure your emails reach the inbox.
Warmy.io provides several powerful tools and features that help optimize deliverability and reduce bounce rates across various ESPs.
Here’s how Warmy.io can support your efforts:
Advanced seed lists to ensure clean lists and genuine authentication
One of the primary causes of hard bounces is sending emails to invalid or non-existent addresses. Warmy.io helps you maintain clean and up-to-date email lists by identifying and removing invalid addresses.
When your email lists only contain valid, engaged recipients, you drastically reduce the chances of hard bounces and avoid sending emails to non-existent or inactive users. This also increases engagement rates by targeting only valid recipients.
On the other hand, you may also want to look into Warmy’s Advanced Seed Lists, which contain genuine email addresses that simulate real human behavior. Emails are opened, read, scrolled through, and clicked, further reducing the chances of landing in spam. Plus, if emails go to spam, they are manually removed and marked as important to improve future deliverability.

Learn more about Warmy’s seed lists here. Or, for a more in-depth look at how Warmy’s seed lists work and what they can do for your email deliverability, check out these articles:
- Email Warmup Alternatives: When Traditional Warmup Isn’t Enough
- Email Engagement How Seed List Helps Improve Open
Authenticate your domains (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Proper domain authentication is critical to prevent emails from being marked as spam across all major ESPs. Warmy.io helps you set up and verify your domain’s SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, ensuring that your emails pass the authentication checks for ESPs like Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, and Zoho.
Warmy.io provides free tools to generate and verify these records:
- Free SPF Record Generator: helps create a valid SPF record to prevent unauthorized email sending.
Free DMARC Record Generator: strengthens email security by preventing phishing and spoofing attacks.
Monitor your presence on blacklists
Having your IP or domain blacklisted can cause significant deliverability issues, leading to high bounce rates. Warmy.io’s free email deliverability test monitors your domain’s status on popular blacklists like Spamhaus and others, so you can address any issues before they affect your campaigns.
🔖 Related Reading: Warmy’s recent research “Are Blacklists Killing Your Emails? A Deep Dive into How They Influence Email Providers” tackles how each ESP uses blacklists in their deliverability measures.
Use Warmy’s AI-powered warmup with customizable preferences
Warmy’s email warmup feature gradually builds trust with ISPs, ensuring that your emails are recognized as legitimate. It does this by mimicking natural email interactions to show ISPs that your emails are trusted and valuable. By warming up your domain before sending at scale, you minimize the chance of SMTP rejections.
The platform is capable of handling up to 5,000 emails per day, making it a robust solution. Additionally, it supports custom templates and multiple languages to personalize the experience for recipients.
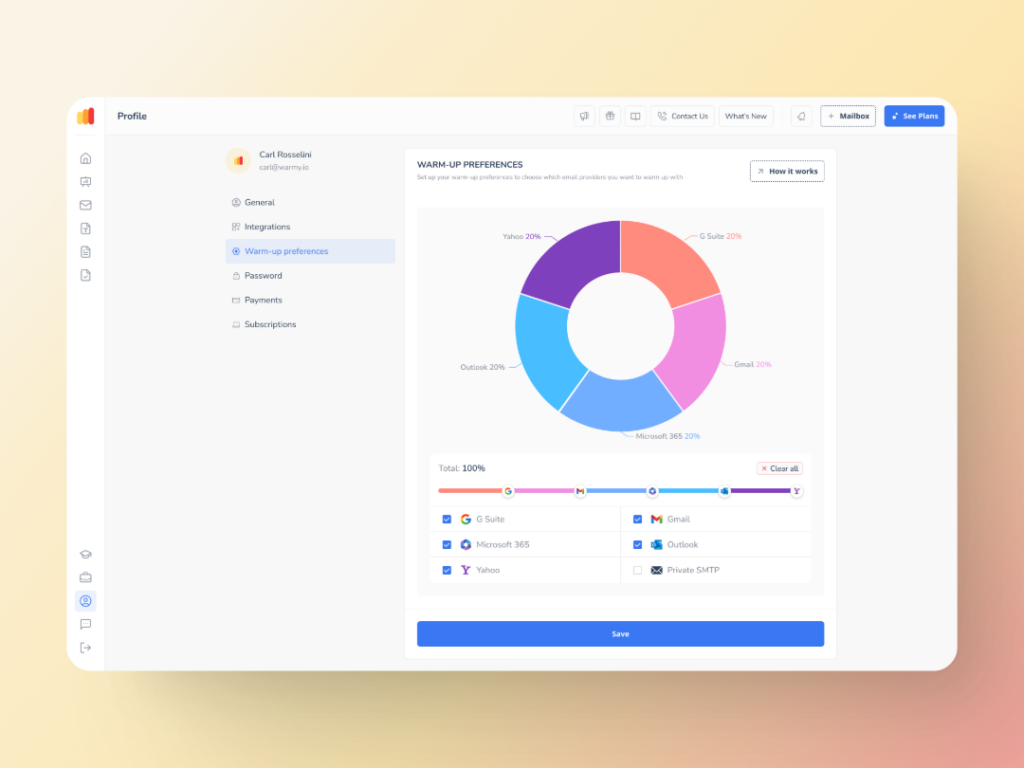
Warmup Preferences is a new feature from Warmy designed to help senders customize and fully control the warmup process from both sender and user levels.
So essentially, senders will be able to customize the warmup’s distribution across different providers. They can also choose if they want to use B2B or B2C customers for engagement patterns to tailor the behavior and insights to their business type. All of these settings can be changed right within the Warmy system for hassle-free customer experience.
Comprehensive data and insights from deliverability tests and domain health hub
To secure your global reputation and avoid bounces, take advantage of Warmy’s free email deliverability test which is critical for evaluating email reputation. It can quickly check if your emails are landing on its intended recipient and shows the percentage of emails that ends in spam, promotions, inbox, and unreceived across major email providers. Plus, it is capable of revealing if your domain or IP is listed anywhere on any blacklists.

Additionally, Warmy’s Domain Health Hub provides a domain health score based on a combination of various factors like authentication, blacklist status, and inbox placement tests.
You’ll also be able to monitor your spam rate trends and overall deliverability performance with weekly or monthly tracking options. It also includes comprehensive DNS status checks to easily validate SPF, DKIM, DMARC, rDNS, MX, and A records for stronger authentication & security.
Let Warmy power up your bounce back
It’s time to stop being captive to bounce rates. Whether it’s monitoring your domain’s health, optimizing sending behavior, or using our built-in deliverability testing tools, Warmy.io streamlines the process, so you can focus on what matters most – your email campaigns.
Ready to take your email deliverability to the next level?
Download the full report to explore more insights and get actionable steps for improving your bounce rates and email performance.











