Email is currently one of the most widely-used forms of communication. These emails need rules to adhere to when they are sent and received to ensure safe passage across the internet. So when you send an email, it actually goes through a rigorous communication process before it can be delivered. Sure, we don’t really see this happening in front of our eyes—but it’s what happens behind the scenes.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) and ESMTP (Extended SMTP) are the two most popular email protocols that determine the way these messages are sent, received, and processed,
SMTP has been the standard protocol since the early days of the internet, and ESMTP is essentially an extension or an upgrade that provides added capabilities such as authentication, encryption and improved error handling.
For certain businesses, depending on how vital email is to their communications, marketing or transactional needs, understanding how SMTP and ESMTP are different from each other may have lasting effects on the business.
This article explains how these protocols work, the reasons why ESMTP is an enhancement over the earlier SMTP, and the advantages of ESMTP implementation to improve the email experience.
What is SMTP?
It is the standard communication protocol used for sending emails over the Internet. It is in charge of managing the exchange of emails between both mail servers and email clients. SMTP works in a command and response way, wherein the sending server sends a command to the receiving server and waits for the response before issuing the next command.
How SMTP works
The sender’s mail server (SMTP client) communicates with the recipient’s mail server (SMTP server) using a series of text-based commands. Some of the key SMTP commands include:
|
SMTP command
|
Meaning
|
|---|---|
|
HELO
|
“Hello.” This initiates communication with the recipient's mail server
|
|
MAIL FROM
|
The client identifies the sender's email address
|
|
RCPT TO
|
The client specifies the recipient of the e-mail
|
|
DATA
|
This asks the server’s permission to transfer data (the body of the email) and does so once it receives a positive reply.
|
|
QUIT
|
This initiates the termination of the connection
|
|
RSET
|
"Reset." The SMTP connection will be reversed to the initial stage
|
|
VRFY/EXPN
|
“Verify”/“Expand” the client checks whether a mailbox or the mailing list is available for message transmission
|
Key features of SMTP:
- Uses port 25 (default) or 587 (submission) for email sending
- Uses a simple command structure (HELO, MAIL FROM, RCPT TO, DATA, QUIT).
- Originally designed for message relay without verifying sender identity.
Limitations of SMTP
SMTP is a simple protocol designed for a specific purpose, but it has a number of limitations:
- Lack of authentication: MTP does not require user authentication, making it susceptible to spoofing and phishing attacks.
- Limited error handling: SMTP offers minimal feedback on message delivery failures.
- No encryption: SMTP sends messages in plain text, which can easily be intercepted and accessed without authorization.
Even though SMTP is still the core of email transmission, these limitations—particularly regarding security and authentication—drove the development of ESMTP.
What is ESMTP?
It is a superset of SMTP that adds functionality and security features. The new standard was introduced to meet the demands of contemporary email communication, such as authentication, encryption, and message error handling.
Key features of ESMTP:
- SMTP authentication. This supports authentication mechanisms (e.g., SMTP AUTH) to verify senders. Users are required to authenticate before sending emails to prevent unauthorized use of email servers.
- Allows encryption via STARTTLS. This provides support for encrypted email transmission, and hence supports data privacy and stops any emails from being intercepted and changed.
- Introduces new SMTP commands such as:
- EHLO: This is the “HELO” alternative. The client logs on and starts the session. If the server supports ESMTP, the session is started successfully. Otherwise, the client must use SMTP.
- SIZE: The server must specify the maximum email size allowed in bytes.
- AUTH: Enables authentication before sending emails
- Supports modern email security protocols. Works seamlessly with SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance).
- Better error handling. Provides detailed status codes for troubleshooting email issues.
Because of these advanced features, ESMTP provides a more secure and efficient method for handling email communication
ESMTP vs SMTP: What are the key differences?
|
Feature
|
SMTP
|
ESMTP
|
|---|---|---|
|
Handshake command
|
HELO
|
EHLO
|
|
Authentication support
|
❌ None required
|
✅ Yes (SMTP AUTH is required)
|
|
Encryption
|
❌ No built-in encryption
|
✅ Yes (Supports STARTTLS for secure communication)
|
|
Command set
|
Basic command set
|
Extended command set
|
|
Spam prevention
|
Minimal
|
Improved with authentication and security features
|
|
Port usage
|
25, 587
|
25, 465, 587, 2525
|
|
Security
|
Prone to spoofing and phishing attacks
|
Supports SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for enhanced security
|
|
Error handling
|
Limited error feedback
|
Provides detailed error messages for better troubleshooting
|
Why ESMTP matters for email deliverability
For businesses, email deliverability is one of the most vital contributors to success. Not being able to transmit emails effectively not only results in bounced emails but also spam filtering and a potential loss of customers. Some of the advancements ESMTP has over SMTP include improved security, authentication, better error reporting, and support for bulk emails. Let’s examine how ESMTP assists in improving inbox placement rates and guarantees that legitimate emails arrive to their correct recipient.
Improved email security
Numerous phishing, spoofing, and spam attacks have become increasingly advanced, placing security as the foremost concern in present-day email communication. SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) has no such encryption and authentication through which emails can be viewed or misused. Meanwhile, ESMTP enhances security through:
- Sender authentication with SMTP AUTH. ESMTP requires a sender to be authenticated before sending an email. It stops unauthorized users from abusing any mail servers, and this helps to limit spam and email spoofing.
- Encryption with STARTTLS. STARTTLS upgrades plain-text email transmissions to encrypted ones, which are less susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks where hackers intercept email content. Encryption protects sensitive data such as financial records, passwords and customer information.
- Adhering to data privacy regulations. Any company that handles customer information is expected to adhere to security regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). By securing sensitive email communications, ESMTP’s authentication and encryption mechanisms can help companies fulfill such compliance requirements.
Better deliverability
Poor deliverability is a common challenge in email marketing and business communications. Unverified emails can end up being marked as spam or even outright blocked. The ESMTP protocol introduces additional commands and features that enhance the deliverability of messages between mail servers.
- SPF, DKIM, and DMARC enhance reputation. ESMTP supports Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC). Such protocols authenticate email senders and help mail servers decide whether to deliver the email to the inbox or reject it.
- Maintaining a clean IP reputation. ESMTP allows businesses to maintain a positive sender reputation by ensuring that email authentication is properly configured. A decent reputation also helps improve inbox placement rates, so more emails go to inboxes as opposed to spam folders.
Enhanced error reporting and troubleshooting
Diagnosing a failed email delivery is one of the hardest problems for IT teams. SMTP’s poor error handling leads to poor visibility into why an email was rejected, delayed, or marked as spam.) ESMTP addresses this by offering detailed error codes and better troubleshooting capabilities.
- Advanced SMTP response codes. Traditional SMTP only provides basic error messages that do not always specify the root cause of delivery failures. Extended response codes allow IT administrators to quickly determine issues and troubleshoot solutions. For example, SMTP errors may be presented as 250, 450, or 550 codes. Meanwhile, examples of Extended SMTP errors include 451 4.7.0 or 501 5.5.4.
- Clearer diagnostic messages. When an email fails to deliver, ESMTP provides more descriptive diagnostic messages when an email does not land in its intended mailbox (examples include if an email was rejected because of an authentication failure, blacklisting, spam filtering, etc.)
Optimizing bulk email sending
Businesses sending high volumes of emails—such as marketing newsletters, transactional emails, and customer support messages—often face challenges related to message size limits, email rejection, and server constraints. ESMTP introduces features that optimize bulk email sending, ensuring efficiency and deliverability.
- SMTP SIZE command for large emails. One important extension of ESMTP is the SIZE command, which enables email senders to query the maximum message size permitted by the recipient’s server before transmitting.
- Efficient large file transfers. Unlike traditional SMTP, which struggles with large email attachments, ESMTP supports 8BITMIME encoding, allowing larger messages and non-English characters to be sent efficiently.
Implementing ESMTP for your mail server
If your organization is highly dependent on email for business communication, you should definitely upgrade from SMTP to ESMTP.
Step 1: Use EHLO instead of HELO
Make sure your mail server supports EHLO instead of HELO. EHLO lets the server declare its ESMTP capabilities.
Step 2: Enable SMTP authentication
Most modern mail servers, including Postfix, Exim, and Microsoft Exchange, support SMTP AUTH. Enable authentication to require valid login credentials for email sending.
Step 3: Implement STARTTLS for encryption
Enable STARTTLS to encrypt email communications. This prevents attackers from intercepting and reading email contents.
Step 4: Use secure ports
While port 25 is still used for email relay, it is often blocked by ISPs to prevent spam. Instead, use:
- Port 587 (SMTP submission with authentication)
- Port 465 (SMTPS – deprecated but still in use by some providers)
- Port 2525 (Alternative secure SMTP port)
Step 5: Monitor and test email deliverability
Regularly test your email deliverability using Warmy’s Free Email Deliverability Test to ensure proper email transmission and security.
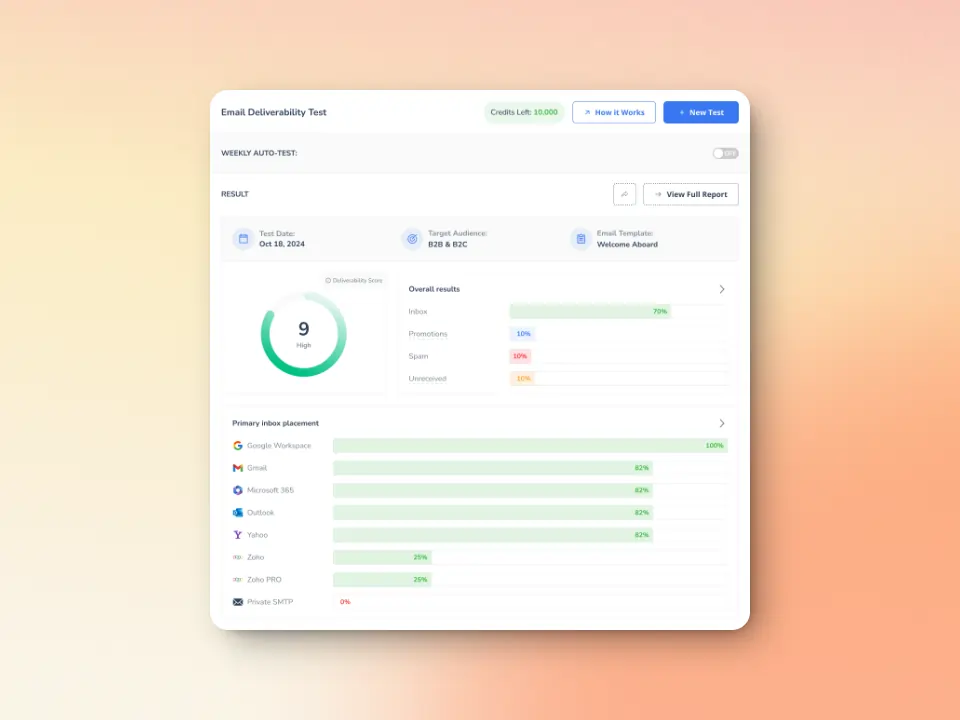
How Warmy.io enhances email deliverability for both SMTP & ESMTP
SMTP and ESMTP may offer the technical underpinnings of email transmission, but effective configuration is only one part of the battle in achieving optimum email deliverability.
Even with ESMTP’s authentication and encryption features, poor sender reputation, spam folder placement, and low inbox rates can still occur. Upgrading to ESMTP is not a guarantee because email deliverability is multi-layered. This is where Warmy.io plays a crucial role in enhancing email performance, security, and deliverability.
Warmy boosts sender reputation for emails sent via SMTP & ESMTP
Warmy.io helps businesses with email sender reputation which is a crucial factor in determining whether an email lands in inboxes or reroutes to the spam folder. It does this by:
- Gradually warming up new email domains before sending high volumes of emails.
- Building positive engagement signals (opens, replies, and positive interactions).
- Using advanced seed lists that contain genuine email addresses that act as seeds to mimic human engagement. These ensure emails are opened and clicked. If emails land in spam, they are manually removed and marked as important.

Optimizing authentication and security
Even though ESMTP offers authentication via SMTP AUTH and STARTTLS, poorly configured authentication records (SPF, DKIM, and DMARC) can lead to email rejections, failed deliveries, or phishing risks. Warmy.io assists businesses by:
- Providing real-time deliverability monitoring and blacklist checks so you can start the delisting process right away if ever
- Offering free SPF Record Generator to authenticate email servers
- Offering DMARC Record Generator for domain protection
Preventing spam folder placements
Even with ESMTP’s enhanced command set and authentication features, emails can still be flagged as spam due to low sender engagement and poor reputation. Warmy.io mitigates this risk by:
- Simulating natural email engagement, such as opens, replies, and positive interactions
- Auto-archiving warmup emails to keep inboxes clean.
- Evaluating emails for potential spam triggers through the Free Template Checker
- Providing deliverability insights and recommendations to avoid common spam triggers.
Why Warmy.io is essential for ESMTP users
Even though ESMTP is a significant improvement over SMTP, email deliverability issues can still arise due to factors like poor sender reputation, lack of engagement, and misconfigured authentication records.
Warmy.io bridges this gap by improving email sender reputation and encouraging authentication. If you’re using ESMTP for business email communication, integrating Warmy.io into your workflow will maximize your email success, prevent emails from landing in spam, and boost sender reputation—all while maintaining compliance with modern authentication and security standards.
Try Warmy.io today for seven days and see for yourself what success looks like.











