Individuals and businesses rely on email for communication for countless reasons. And so it can be incredibly frustrating when your emails don’t make it to their intended target.
For instance, SMTP Error 554 5.6.0 is one that the email sender never wants to encounter. That means an email was rejected because of content issues. The recipient’s email server has rejected the message as it violates filtering policies—such as suspected spam-like content, incorrect formatting, or unsupported attachments.
For email marketers, this mistake could result in losing email outreach opportunities, decreasing engagement rates, and unnecessary time being spent developing campaigns. IT and email security teams might have trouble figuring out how come their legitimate emails are being rejected, while SaaS email providers need to ensure that their email generated on their platforms always lands in inboxes.
What is SMTP Error 554 5.6.0?
SMTP Error 554 5.6.0 is a permanent failure response. It indicates an email has been rejected because of content-related issues. That usually means the recipient’s email server has, upon reviewing the message, determined that it did not meet its filtering criteria and so was blocked prior to delivery. Unlike temporary errors (such as 4.x.x codes), indicates that the message was rejected outright and that it won’t even be retried.
This error can be a roadblock because it prevents emails from reaching inboxes, affecting marketing campaigns, customer communication, and business functioning.
Common causes of SMTP Error 554 5.6.0
When an email is rejected due to SMTP Error 554 5.6.0, it’s typically because the content of the message violates the recipient’s filtering rules. Below are the most common reasons why emails get blocked under this error code.
Presence of spam-like content
Email providers use spam detection algorithms that analyze messages for patterns associated with unsolicited or malicious emails.
- Use of trigger words and phrases: Certain words or phrases (e.g., “Make money fast,” “Free trial,” “Limited-time offer”) are often flagged by spam filters. Emails containing too many of these can be rejected.
- Excessive use of capital letters, special characters, or excessive links: Messages with ALL CAPS subject lines, excessive exclamation marks (!!! ), or an unusually high number of links may flag spam filters.
- Email formatting issues: If the email doesn’t have an appropriate text-to-image ratio (imagine an email that contains nothing more than an image and no text), this can be problematic as spam.
Take an email promotion with a subject line “FREE MONEY!!! CLICK HERE NOW!!! ”This will likely be blocked because of spammy language and formatting.
🔖 Related Reading: Why are My Emails Going to Spam or Junk? [Solved]
Unsupported attachments
Many email providers enforce limits on attachment sizes and types (for example, Gmail allows 25MB attachments). If an email exceeds these limits, it might simply be rejected temporarily. But if an email has any risky attachment then it could generate SMTP Error 554 5.6.0 and therefore it is blocked and rejected.
- There is also the case of attachments with extensions such as .exe, .js, .bat and .vbs.These are frequently identified as security threats.
- Certain email services refuse compressed files (ZIP, RAR, etc.), particularly when they contain several files or are encrypted.
For example, an IT team emailing a ZIP file protected by a password within it that contains company credentials may see the email get flagged and blocked, because attachments that are password-protected are often deemed to be a security risk.
Improper email formatting
Emails must be properly structured to be accepted by modern email security filters.
- HTML vs. plain text emails: HTML emails that are poorly formatted or lack a plain-text version can be rejected.
- Use of broken or incomplete HTML code: If an email contains unclosed tags, missing alt attributes for images, or inline styles that break, it may fail validation checks.
Example: A newsletter with misaligned tables, missing closing HTML tags, and non-standard encoding might be rejected by corporate email servers that enforce strict formatting policies.
Email authentication issues
Email authentication protocols help verify that a sender is legitimate. Receiving servers may reject emails if authentication records are missing or misconfigured to prevent a spoof attack or phishing attack.
- Missing or incorrect SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records: These are three types of authentication mechanisms that determine if an email came from a valid source. If these records are misconfigured or absent, emails may be rejected.
- Authentication failures can lead to email rejection: Some providers have strict email security policies and reject any message that fails authentication.
- Checking DNS records for misconfigurations: DNS errors, including outdated or missing records, can cause email servers to reject messages.
Example: A SaaS platform sending transactional emails via a third-party SMTP provider (e.g., SendGrid) without proper SPF/DKIM alignment may experience mass email rejections.
🔖 Related Reading: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Boosting Email Security and Deliverability
Blacklisted sending domain or IP
If a domain or IP address belongs to an email sender that has ended up on a blacklist, the email provider can automatically reject their messages to block spam from reaching a user.
Many email providers reference real-time blacklists (RBLs) such as Spamhaus, Barracuda, and UCEPROTECT. If a sender’s IP or domain is listed, messages are often blocked. If blacklisted, senders may need to request delisting and improve sending practices before regaining reputation.
Example: A company’s marketing emails get rejected across multiple email providers because their domain was blacklisted after a high volume of emails bounced or were marked as spam.
How to fix SMTP Error 554 5.6.0
1. Review and optimize email content
To prevent rejections, ensure your emails follow best practices. Use a spam checker before sending emails. Before hitting “send,” run your email through a spam testing tool to analyze spam score, formatting, and potential triggers, helping you adjust your email before delivery.
- Use a proper text-to-image ratio: Avoid emails that contain only images with no supporting text.
- Keep email subject lines natural: Avoid all caps and excessive punctuation (e.g., “🚨URGENT: GET FREE MONEY NOW!!!🚨”).
- Limit the number of links: Too many links can make an email look like spam. Keep them relevant.
- Use natural language: Write emails as if you’re speaking to a person, not as a sales robot.
- Avoid triggering words and spam-like formatting like “Make money fast,” “100% free,” “Limited-time offer,” or “Winner!”
2. Check and remove unsupported attachments
Most email providers block or screen emails that contain dubious attachments. Here are the best practices you can follow to avoid SMTP 554 5.6.0 errors.
- The file types need to be standard. Stick to PDF, DOCX, PNG, or JPG.
- Avoid sending executable files (.exe, .js, .bat) as they are frequently blocked.
- Avoid compressed files (. zip,. rar), since they may be automatically rejected by some email servers.
- Rather than attaching large files, create links to them in cloud storage such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive. This approach reduces email size, prevents rejection, and allows tracking of file access.
3. Ensure proper email formatting
Poorly formatted emails can be flagged as spam or rejected by email security systems. To avoid this, follow these steps:
- Structure HTML emails correctly by ensuring a balanced mix of text and images as well as well-structured tables instead of CSS-heavy emails. Also include an alternative plain-text version of your email.
- Use email testing tools to check formatting, such as Litmus (previews email rendering across different devices) or Email on Acid (helps businesses test and optimize HTML emails.
4. Authenticate your email domain
If authentication records are missing or incorrect, emails may be rejected as suspicious or fraudulent.
- Set up SPF (Sender Policy Framework). Ensure your SPF record allows your email provider’s servers to send emails on your behalf. (Example SPF Record: v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all)
- Enable DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). DKIM adds a cryptographic signature to emails, verifying their authenticity. (Example DKIM Record: v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=public-key)
- Implement DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance). DMARC tells recipient servers how to handle authentication failures. Example DMARC Record: v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:reports@yourdomain.com
5. Monitor your domain reputation
Your domain’s reputation directly impacts email deliverability. If your domain or IP is blacklisted, your emails may be rejected before they even reach spam filters.
Use tools like MXToolbox and Spamhaus to check if your domain is on a blacklist. Then, if in case your IP or domain is blacklisted, identify the blacklist and visit their website. Follow their delisting instructions (some require verification or an explanation). Then, improve sending practices to avoid getting blacklisted again.
🔖 Related Reading: Email Domain & IP Blacklist Removal: 5 Steps to Delist
Make sure your email content game is top-notch with Warmy’s email deliverability solutions
Avoiding SMTP Error 554 5.6.0 isn’t just about fixing rejected emails and trying again—it’s about preventing them in the first place. If ESPs continue rejecting your emails, the long-term impact can be detrimental to the business as a whole. Warmy.io is a leading AI-driven platform that ensures your emails consistently reach inboxes, helping you avoid rejections due to content-related filtering issues. Here’s how Warmy.io helps eliminate these risks:
Email warmup and advanced seed lists for building strong sender reputation
One of the most effective ways to avoid content-based rejections is by ensuring your email account has a strong sender reputation. Warmy.io’s AI-driven email warmup combined with advanced seed lists have redefined email warmup. The capabilities go beyond traditional warmup:
- Mimicking real human interactions: Sending, clicking, replying, and marking emails as important to improve engagement. In case an email still finds its way to spam, it is manually removed and marked as important—teaching ISPs that you are credible and legitimate. (Related Reading: Email Engagement How Seed List Helps Improve Open & Click Rates)
- Gradually increasing email volume: This prevents ISPs from flagging your emails as spam
- Customizing warmup content: Matches industry-specific content, reducing the chance of triggering spam filters.
- Allowing up to 5,000 warmup emails per day: This ensures consistent and robust inbox placement.
Expanding warmup process: Warming up using other providers that previously couldn’t be warmed up (Mailchimp, Shopify, Omnisend, and Klaviyo, etc.)
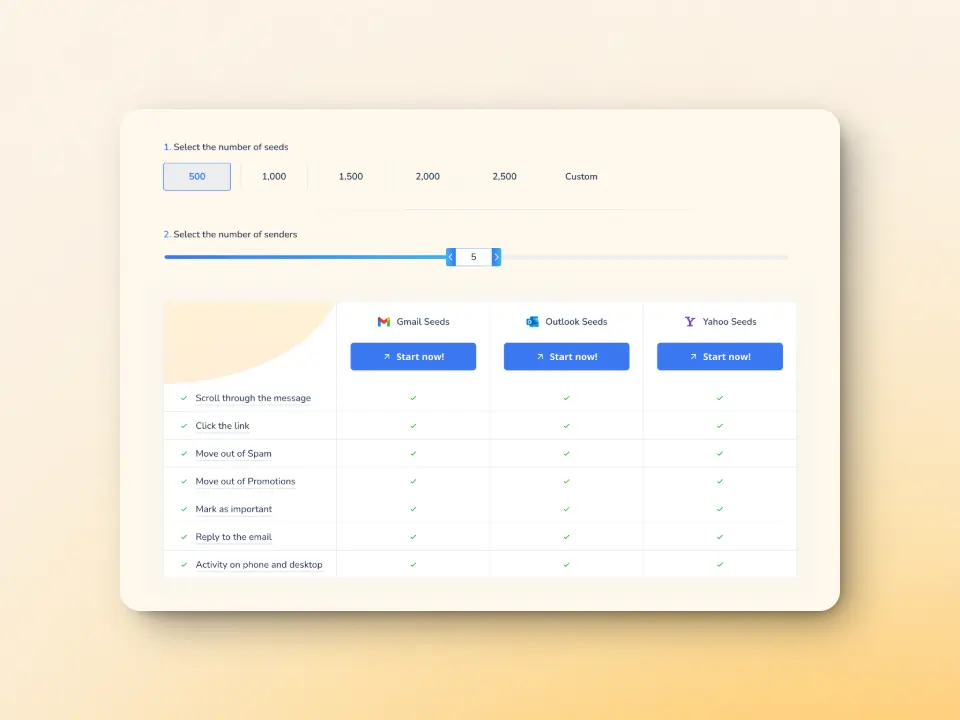
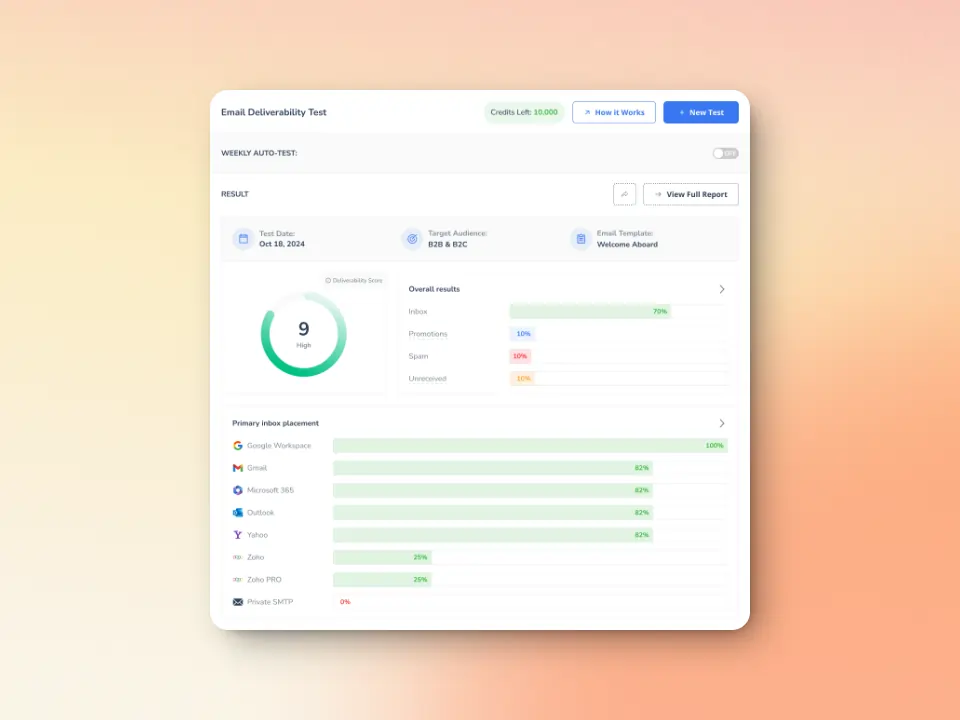
Deliverability testing: Identify and fix content issues before sending
Warmy.io’s Email Deliverability Test allows you to analyze your emails so you can make sound decisions on how to move forward. It provides:
- A full breakdown of inbox placement: Know if your emails land in the inbox, spam, or promotions tab.
- Spam trigger analysis: Identify words, formatting, and content issues that could result in rejection.
Blacklist checks: Ensure your domain or IP isn’t on a blocklist that could affect deliverability.
Content optimization tools to avoid formatting and spam triggers
Warmy.io provides several free tools to fix content-related issues:
- Template checker to evaluate your email templates for potential spam triggers.
- Cold email sequence builder to help structure your outreach emails properly to avoid rejection.
Authentication setup: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configuration
Missing or incorrect SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records can cause email rejections due to authentication failures. Warmy provides:
- Free SPF Record Generator: Helps create SPF records to validate sending servers.
- Free DMARC Record Generator: Helps implement DMARC policies to prevent spoofing.
Monitoring and improving domain health
Warmy provides one dashboard where senders can monitor deliverability at the domain level—giving greater control, transparency, and efficiency when it comes to performance. The Domain Health Hub grants the following:
- Domain Health Score: A rating based on factors like DNS authentication, Google Postmaster data, inbox placement, etc.
- Warmup performance insights: This includes data like spam rates, inbox placement, and other trends on a weekly or monthly basis
- Comprehensive DNS status checks: For validation of SPF, DKIM, DMARC records for stronger security
Avoid SMTP 554 5.6.0 Errors with Warmy.io and achieve overall email success
SMTP Error 554 5.6.0 can be a major roadblock but by understanding its causes—whether it’s spam-like content, improper formatting, authentication failures, or domain reputation issues—you can take proactive steps to fix and prevent these rejections.
With Warmy.io, you get the knowledge and the tools to ensure your emails land in inboxes consistently and securely. Don’t let deliverability issues hold you back! Get started with Warmy.io today and ensure your emails always reach the right audience.











