Email transmission via the internet is made possible by the foundation of email communication, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, or SMTP. Efficient email management depends on the SMTP settings being configured correctly, which guarantees that messages are sent and received consistently without problems like delays or data loss.
Among the most well-known email services, Gmail lets users send emails over its SMTP server. When it comes to deliverability, a free deliverability test is a good first step to uncovering any existing issues.
When using Gmail for SMTP, customers may take use of all the security and dependability that Google provides, including spam prevention, easy setup, and high delivery rates. With effective and safe email handling, this configuration improves the whole communication experience for both personal and business contact.
What is a Gmail SMTP Server?
Simple mail transfer protocol, or SMTP, is an Internet email delivery protocol. Emails are correctly routed from the sender’s email server to the recipient’s email server thanks to its provision of the required instructions for email servers to communicate with one another. Effective and dependable email delivery depends on SMTP to manage both sending outgoing emails and relaying emails from server to server.
Sending emails with Gmail accounts is made possible via Google’s implementation of the SMTP protocol—the Gmail SMTP server. Users who want to send emails using their Gmail interface or through third-party apps utilizing their Gmail credentials may find this service especially helpful.
Here are the particulars regarding the SMTP server of Gmail:
- SMTP server address: smtp.gmail.com
- SMTP username: Your full Gmail address (e.g., yourusername@gmail.com)
- SMTP password: Your Gmail password
- SMTP port (TLS): 587
- SMTP port (SSL): 465
Want to know more? Read also: What is SMTP and how does the SMTP server work?
Why Should You Use Gmail as an SMTP Server?
There are several advantages to using Gmail as your SMTP server compared to other SMTP providers — mainly in terms of reliability, security, and ease of use.
Here are some of the most important reasons why individuals and companies can use Gmail SMTP server:
- It is highly reliable. Gmail is supported by the infrastructure of Google, the second-largest IT company in the world, which is famous for its high reliability, scalability and resilience systems. This makes sending emails reliable, with high availability and little downtime.
- It has strong security features. Industry-leading security features in Gmail include TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption of emails in transit by default, strong defenses against phishing, and two-factor authentication (2FA). Sensitive data is protected through these measures and the likelihood of an unauthorized access to the email account is decreased. Read more here: SSL and TLS Certificate Errors in Email Servers: How They Impact Deliverability
- Google’s sophisticated algorithms help in identifying and eliminating spam and damaging emails. This not only protects the user’s inbox but also preserves their email account’s reputation, reducing the chances of other email servers marking their outgoing emails as spam.
- Gmail’s SMTP server is a quick hit with many of the SMTP-capable apps and devices you know. This simplifies configuration as users can send emails from CRM systems, third-party email clients, or even custom applications using their Gmail account.
- It is easily scalable. Gmail’s infrastructure can scale email volumes to the business as needed, without users needing to manage their own email servers. It is perfect for both big and small companies due to its scalability.
- It is cost-effective. As Gmail is a part of the wider Google Workspace services that also comprise other useful tools such as Google Drive, Google Calendar, Google Docs, using it as an SMTP server can be budget-friendly for single users and small ventures as well. Purchasing a separate email delivery service might be pricier than this all-in-one service.
- Because emails go out through Gmail’s SMTP server, they benefit from Google’s strong email service reputation. Thanks to this reputation, deliverability rates increase, and emails are less likely to end up in recipients’ spam folders.
How to configure Gmail SMTP server settings
Step 1: Enable two-factor authentication (recommended)
For added security, it is highly recommended to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your Gmail account. This can be done through your Google account settings under the “Security” tab.
Step 2: Generate an app password
- Go to your Google Account settings.
- Select “Security” from the left sidebar.
- Under “Signing in to Google,” find “App Passwords” and click it.
- You might need to sign in again to access this page.
- At the bottom, click “Select app” and choose the app you’re using.
- Click “Select device” and choose the device you’re using.
- Click “Generate” and follow the instructions to generate the app password. This is what you will use as the SMTP password.
Step 3: Configure SMTP settings in your email client
With your Gmail account and app password ready, you can now configure the SMTP settings in your email client:
- SMTP server address: smtp.gmail.com
- SMTP username: Your full Gmail address (e.g., yourusername@gmail.com)
- SMTP password: The 16-character app password generated if you have 2FA enabled, otherwise your Gmail password.
- SMTP port (TLS): 587
- SMTP port (SSL): 465
- Security: Choose TLS/SSL based on the port you are using.
Step 4: Enter additional settings (if needed)
Some email clients require additional settings or adjustments:
- Require sign-in. Check this option, as authentication is required to send emails through Gmail’s SMTP server.
- Outgoing server requires authentication. Yes, it’s typically checked by default.
- Use the same settings as my incoming mail server. Often selected if you’re using the same service for incoming and outgoing emails.
Step 5: Test the configuration
Send a test email after configuring your email client’s SMTP settings to make sure everything is operating as it should. To be sure the outgoing emails are being sent flawlessly, check them.
How to configure Gmail POP3 settings
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version 3 and is used to retrieve emails from a remote server to a local client.
POP3 downloads mail from a server on a single computer and deletes the mail from the server. This allows you to work with your emails without net connection to the Internet region too.
However, as major systems delete emails from the server after downloading (unless configured specifically to keep copies on it), POP3 is not the most convenient way of viewing your email from multiple devices.
When to use POP3
Emails from a distant server are retrieved to a local client using the email access protocol POP3, or Post Office Protocol version 3.
POP3 copies emails from a server to a single PC and subsequently removes them from the server. This enables you to manage your emails locally or with restricted internet access. Nevertheless, unless set up especially to leave copies on the server, POP3 is not the best option for viewing your email from several devices because it usually deletes the emails from the server after downloading.
Here’s a quick summary of how to know if you should use POP3:
- You need to access your emails offline.
- You prefer all your emails stored locally and not on the server.
- You use only one device to check your emails.
- You want to ensure a clean server inbox, with all emails stored on your personal computer.
How to enable and configure POP3 in Gmail
Step 1: Enable POP in Gmail
- Sign in to your Gmail account.
- Click on the gear icon in the upper right corner to open Settings.
- Go to the “See all settings” button.
- Navigate to the “Forwarding and POP/IMAP” tab.
- In the “POP download” section, choose the option “Enable POP for all mail” or “Enable POP for mail that arrives from now on” depending on your preference.
- Below this, in the “When messages are accessed with POP” section, select what you want Gmail to do with your messages after your POP client or device has accessed them. To keep copies in your Gmail inbox, choose “keep Gmail’s copy in the Inbox.”
- Click on “Save Changes” at the bottom of the page.
Step 2: Configure your email client
- POP server: pop.gmail.com
- Port: 995
- Username: Your full Gmail address (e.g., yourusername@gmail.com)
- Password: Your Gmail password (If you have two-factor authentication enabled, you will need to generate and use an app-specific password.)
- Security: SSL (Use SSL for encrypted communication or select ‘Use secure connection (SSL)’).
Step 3: Configure additional settings
Should you intend to access your email from several devices, make sure your email client is configured to leave a copy of the emails on the server. Usually located in the advanced options area of your email program is this option.
Step 4: Test your setup
Test your POP settings by sending yourself an email. Confirm operation by verifying the sending and receiving capabilities.
How to configure Gmail IMAP settings
IMAP is a protocol to access email messages (stored in your mail server) from a remote client. IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) allows two-way synchronization between an email client and the mail server as opposed to the older Post Office Protocol (POP) which merely downloaded email from the server to the PC.
Whatever you do on the email client is reflected on the server. So if you read an email on your smartphone, for instance, it also shows up as “read” on your desktop client.
Advantages of using IMAP
For viewing your emails on several devices, IMAP synchronizes the email clients and ensures all data across all devices are the same.
- Internet-based. Since emails are kept on the server, they are available from any device with an Internet connection.
- Space economy. Emails are saved on the server and are not downloaded locally on devices (unless otherwise noted).
- Centralized management. Organize your emails into folders, delete them, or mark them as read all right on the server, saving you from having to do it on each device.
- Saves bandwidth. Selective downloading lets you save bandwidth by letting you see headers and choose which emails to download and read.
How to configure Gmail IMAP settings
Step 1: Enable IMAP in Gmail
- Sign in to your Gmail account.
- Click on the gear icon in the upper right corner to open the Settings menu.
- Go to the See all settings.
- Click on the Forwarding and POP/IMAP tab.
- In the IMAP Access section, select Enable IMAP.
- Click Save Changes at the bottom of the page.
Step 2: Configure your email client
To set up your email client, use the following settings:
- IMAP server:
imap.gmail.com - Port: 993
- Require SSL: Yes (Use SSL/TLS)
- Username: Your full Gmail address (including
@gmail.com) - Password: Your Gmail password (If you use two-factor authentication, you might need to generate an app-specific password.)
- IMAP server:
Step 3: Adjust IMAP settings in Gmail (optional)
After enabling IMAP, you can customize how IMAP behaves. For instance:
- Folder size limits. You can limit the number of messages synchronized to your mail client to increase performance.
- Label handling. Choose which Gmail labels are visible in your IMAP client. This is useful if you don’t want certain emails or categories to sync with your email client.
Here’s what you should do:
- In the Gmail settings under the Forwarding and POP/IMAP tab, you can find various options for handling IMAP.
- Customize the settings according to your preferences and click Save Changes.
G Suite/Google Workspace SMTP relay settings
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) SMTP relay service allows you to send emails from your organization using authenticated SMTP credentials or validated IP addresses. If your company sends out a lot of mails or communications, then this service comes in really handy.
Differences between general Gmail and Google Workspace SMTP settings
- Authentication. Google Workspace SMTP relay does not require sender identity verification through the username and password if you authenticate using the IP address.
- Sending limits. Google Workspace SMTP relay has higher sending limits compared to general Gmail SMTP settings, which is ideal for enterprises and mass mailing scenarios.
- Use case. Google Workspace SMTP relay is intended for business and organizational use, whereas Gmail SMTP is more suited for personal email communication.
Configuration guidelines for G Suite/Google Workspace users
Step 1: Enable SMTP relay in Google Workspace admin console
- Go to the Google Admin console (
admin.google.com). - Click on Apps > Google Workspace > Gmail > Advanced settings.
- In the Routing section, find the setting for SMTP relay service and click Configure or Add another.
- Enter the configuration information for your SMTP relay:
- Name of the SMTP relay service
- Allowed senders: Choose between only addresses in your domains or any addresses.
- Authentication: Choose whether to require SMTP Authentication or to identify by IP address.
- Encryption: Select “Require TLS encryption”.
Step 2: Configure your email server or application
Use the following settings in your email server or application that will connect to the Google SMTP relay:
- SMTP server address:
smtp-relay.gmail.com - SMTP port: Typically 587 (with STARTTLS) or 25; SSL is not supported.
- Authentication (if required): Use Google Workspace domain credentials.
- SMTP server address:
Step 3: Update firewall settings
Ensure that your firewall rules allow outgoing connections to smtp-relay.gmail.com on the appropriate ports.
Key restrictions on Gmail SMTP use
Sending limits. Gmail limits the amount of emails that you can send in a day to just 500 messages for personal Gmail accounts and 2,000 messages for Google Workspace accounts. This is set to prevent spamming and preserve the integrity of the service.
Attachment size. The 25MB limit is for attachments with email sent over SMTP. Some larger files must use Google Drive instead.
Connection limits: Gmail also has limits for simultaneous connections in its SMTP servers. Users should normally have no more than 2 concurrent connections.
Authentication and encryption. Gmail requires SMTP connections to be secured by SSL/TLS for email transmissions. Without encryption, you won’t be able to send mail using smtp.
Recipient limits. It limits the number of message recipients per message and per day. For instance, one email may be sent to up to 100 email addresses total including To field, Cc field, and Bcc field.
Spam and abuse monitoring. Gmail also watches outgoing emails for spam and abusive messages. Accounts identified as sending spam or malicious content may be suspended or limited.
Explanation of 'less secure apps' in Gmail
In Gmail’s world, “less secure apps” are programs and gadgets that send and receive email using less secure, outdated sign-in technology. These apps typically, literally, log in to your Gmail account with your username and password; they don’t implement the latest security features, aka OAuth 2.0, which add additional layers of security.
Google actually classifies these apps as “less secure,” because they’re more vulnerable to takeover attempts. If they were able to obtain your username and password, no other authentication process (such as two–factor authentication) was enough to prevent someone from accessing your email.
Steps to enable or disable access
Google has progressively tightened security by discouraging the use of less secure apps. Here’s how you can manage the settings related to less secure apps:
Step 1: Access your Google account settings
- Sign in to your Google Account.
- Navigate to the Security section of your account settings.
Step 2: Manage access for less secure apps
For personal Gmail accounts: As of late 2020, Google no longer allows users to enable the “Less secure apps” setting for new devices. For accounts that had this setting enabled before, it was phased out starting June 15, 2020. Users are encouraged to use more secure methods to access their accounts, such as setting up App Passwords (which requires two-factor authentication) or using OAuth 2.0.
For Google Workspace accounts: Admins can control whether users in their organization can use less secure apps:
- Go to the Admin console (
admin.google.com). - Click on Security > Basic settings.
- Under “Less secure apps”, choose the option that suits your security needs:
- Allow users to manage their access to less secure apps
- Disallow access to less secure apps (recommended for enhanced security)
- Go to the Admin console (
Step 3: Encourage secure app usage
Regardless of the settings, encouraging the use of more secure applications and authentication methods is recommended. Using apps that support OAuth authentication will significantly enhance your account’s security.
Implications for email security
Enabling less secure apps:
- Pros: Allows older or simpler mail clients and devices to access Gmail.
- Cons: Increases the vulnerability of your account to unauthorized access, as it only relies on username and password for authentication.
Disabling less secure apps:
- Pros: Greatly improves security by ensuring that only applications with modern authentication methods can access your account.
- Cons: May prevent some older devices and applications from accessing your Gmail account unless they are updated or replaced.
Troubleshooting Gmail SMTP server configuration
Setting up Gmail’s SMTP server in third-party email clients can produce a few standard issues from time to time. The following list of frequent issues encountered by users:
Authentication errors. These happen when either an app-specific password is not being used or two-factor authentication is being activated but there’s something wrong with either the username or the password.
Failure or timeout of connection. These are issues that happen when the SMTP server settings do not match, like if the server address or port number is incorrect.
SSL/TLS Errors. Incorrect security configurations can prevent a secure connection to Gmail’s SMTP server. Read more here: Why SSL & TLS Certificate Errors Are Hurting Your Email Deliverability
Sending restrictions reached. If you exceed Gmail’s strict daily volume limits, your SMTP service may be momentarily blocked.
Blocked by Google for security reasons. Occasionally, particularly from unfamiliar devices or locations, Google may prohibit an attempt to log in using SMTP if it appears strange or less secure.
Enhancing email campaign success with Warmy.io
Warmy.io is an email deliverability solution designed to increase the likelihood that your emails will end up in recipients’ inboxes instead of their spam folders—therefore increasing the success rate of your email campaigns. Here’s how Warmy does it:
AI-powered email warmup
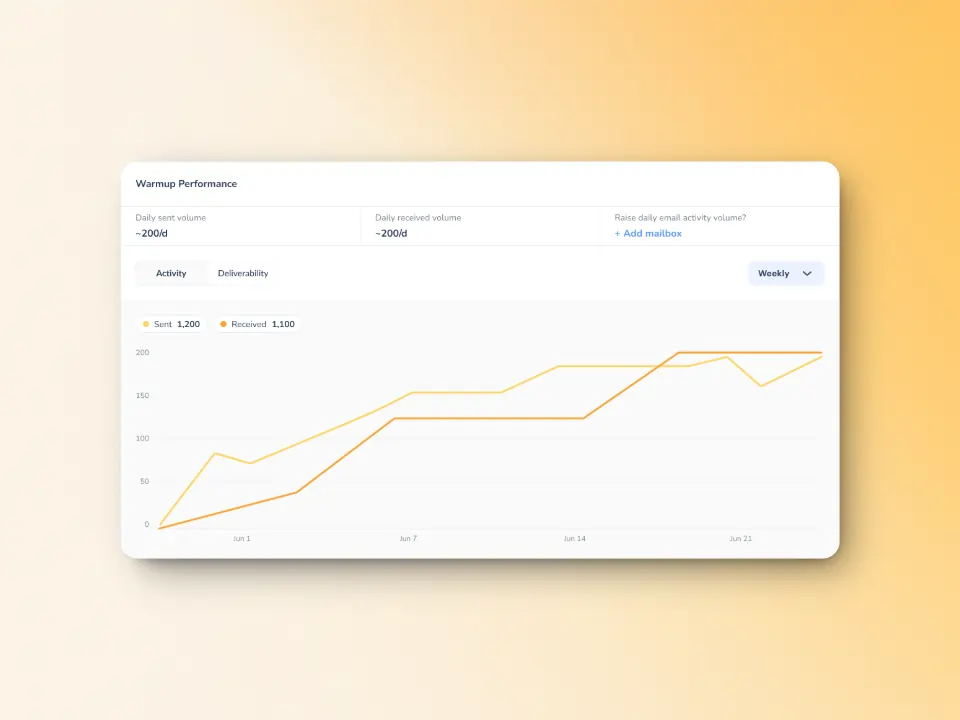
Slowly and progressively ramps up sending volume to build trust with mailbox providers.
Mimics actual human behaviour — emails get opened, replied to, and flagged as important, training email service providers that your emails belong in inboxes.
Works with more than 30 languages so your emails would seem human and contextual to international customers.
Enhanced warmup process tailored for you
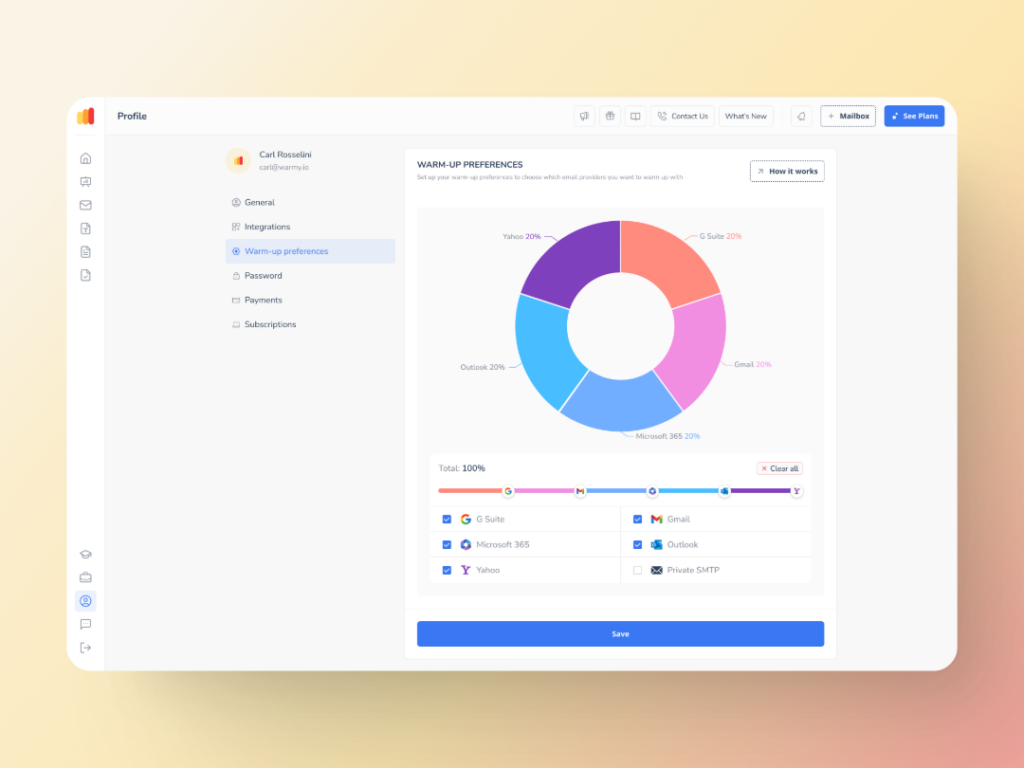
With the ability to control the warmup process from the Sender and User side, Warmup Preferences is one of the most powerful features of Warmy.
Senders are now able to tailor the warmup distribution for a range of different providers. They also have the option of choosing between B2B or B2C customer engagement patterns, which helps them customize the behavior and insights as per their business requirement.
The Warmy system also allows users to fine-tune all these settings in perfect detail without leaving the platform—ensuring everything works perfectly and smoothly.
Advanced seed list ensures strong inbox placement
Warmy’s Email Seed List addresses more behavioral aspects of engagement, telling email providers loud and clear that this email list loves your emails. It features real, live email addresses from top providers such as Google, Outlook, and Yahoo, updated weekly to guarantee real engagement.
Unlike static seed lists where recipients are simply sent messages, Warmy’s system is dynamic and simulates real recipient behavior:
Your emails are opened and scrolled through, all powered by advanced AI that mimics true engagement.
Embedded links are clicked by default to give a clear signal to email providers that your emails are authentic, enhancing sender reputation.
In case any emails land in the spam box, they are retrieved and marked them important
To further enhance your deliverability, the API Endpoint for Established Seed List allows you to effortlessly retrieve, manage, and configure your seed list splits while directly integrated into your system—reducing errors and saving valuable time.
Email deliverability testing to detect issues before they cause SMTP errors
Warmy.io offers a free email deliverability test that helps identify potential problems before your emails get rejected.
- Inbox Placement Testing determines whether your emails are landing in Inbox, Spam, or Promotions tabs.
- Blacklist monitoring detects if your domain or IP is on a spam blacklist, a common reason for SMTP errors.
- SPF, DKIM, and DMARC verification to ensure authentication records are configured correctly to reduce deferrals.
Example: If your emails are frequently rejected or delayed, Warmy.io’s diagnostic tools can pinpoint DNS misconfigurations or authentication failures, allowing you to fix them proactively.
Maximize email deliverability with Warmy.io
Sending your emails safely and successfully requires correct configuration of the Gmail SMTP settings.
To avoid problems including authentication failures or connection failures, it is imperative to carefully follow the setup procedures and confirm every configuration parameter. Correct configuration of these variables can greatly increase the effectiveness of your email delivery and general communication.
Recall that in the modern digital age, professional and efficient communication is based on a well-configured email client. Thus, to maximize the efficiency of your email exchanges, make sure your Gmail SMTP settings are set up correctly.
But it’s not the only factor, it’s more like a step. There are other aspects of email deliverability that you must focus on, such as sender reputation, avoiding spam filters, and authentication protocols among others.
Try Warmy.io for free today (up to seven days—no credit cared required) or book a demo with an expert for a more tailored walkthrough.











