Email addresses fall into two main categories: generic and role-based.
A generic email address is a catch-all address. It represents a team or department rather than a specific person. Examples are “info@company.com” or “support@service.com.” This type of email is often used to receive general inquiries or customer service requests.
Role-based email addresses are assigned to specific roles within a company, like “manager@company.com” or “hr@firm.com.” They focus on a particular job or function rather than a single person. Knowing the difference between these types helps businesses manage email communication better.
What are Generic Email Addresses?

A generic email address typically represents a broad category or function rather than an individual within an organization. It serves as a general point of contact, ensuring that messages reach the company without being directed to a specific person.
Generic email addresses, such as “info@company.com” or “support@brand.com,” offer a centralized point of contact, ensuring that inquiries or feedback are received and can be appropriately routed within the organization.
Such addresses present a unified front, often giving the impression of a well-organized business structure.
Reasons Businesses Opt for Generic Email Addresses
✅ Efficiency. By directing general inquiries to a single address, businesses can streamline their communication processes, ensuring that no message goes unnoticed.
✅ Flexibility. As these addresses aren’t tied to individual employees, there’s no need to update external contacts if there’s a change in personnel.
Common Examples of Generic Email Addresses:
- contact@company.com
- helpdesk@serviceprovider.com
- sales@retailer.com
- feedback@organization.org
- info@company.com
- hello@startup.net
- inquiries@business.com
- support@serviceprovider.com
- help@platform.org
- questions@organization.net
- assistance@tool.com
- general@enterprise.org
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Generic Email Addresses
Generic email addresses are ideal for many corporations, and other businesses. Here are the following advantages:
- Centralized Point of Contact
Having a generic email address is ideal for businesses as it helps maintain a singular point of contact. Clients, customers, and potential prospects can easily find the company’s contact information, ensuring streamlined communication with the guarantee that messages are received by the correct team or person.
It enables a centralized point of contact, making it easier for clients, customers, and potential
- Brand Consistency
Using a standard format for email addresses, like “support@brand.com,” looks professional and helps reinforce the brand’s identity.
- Simplifying Tracking and Managing of Messages
All emails come to one place instead of being spread across different inboxes.
However, there are some downsides in using generic emails.
- Missed Emails
Since generic emails usually receive a high volume of messages, it is probable that the administrator of these emails can miss important emails.
- Lack of Human Connection
Another drawback is the lack of human connection, or personal touch — which is a big deal for many people who want to connect to a human being to resolve an issue or answer an inquiry. This can impact relationship-building and damage lead generation.
- Potential Clutter
Without good organization, a generic inbox can quickly get cluttered, making it hard to find priority messages and respond promptly.
Best Generic Email Address Practices For Businesses
Selecting and managing a generic email address is a crucial aspect of business communication. This helps you avoid clutters of important messages and ensure that your communication is streamlined.
1. Choose the Right Generic Email Address
Pick a generic email address that fits its purpose. For example, “support@company.com” works well for customer support. For sales inquiries, “sales@brand.com” is a good choice.
Make sure the address is easy to remember. It should match your brand and clearly show its purpose.
2. Organize Incoming Emails
A generic email can get a lot of messages. To keep things organized, set up filters to sort emails by topic or sender. Use labels to make them easy to find, and archive old emails to keep the inbox clean.
Consider using tools that automatically sort messages or reply to common questions. This can save time and improve efficiency.
3. Respond Quickly and Follow Up
One of the primary concerns with generic email addresses is the potential delay in responses. To mitigate this, businesses should set clear response time targets.
Send an automatic reply to confirm receipt of each email. This reassures the sender that you’ve received their message and will reply soon.
Check the inbox regularly and forward emails to the right team if needed. Setting reminders for follow-ups ensures that no communication thread is left hanging.
What are Role-Based Email Addresses?
Role-based email addresses are linked to a specific job or department, not a person. They serve a functional purpose rather than being personal.
One key advantage is that they stay the same, even if someone new takes over the role. This keeps communication consistent, no matter who’s in the position.
Role-based emails are also broad. They cover a team or department’s work, not just one individual’s tasks. This makes them useful for group responsibilities and shared communication.
Examples of Role-Based Email Addresses and Their Specific Purposes:
1. “support@company.com”. This address is typically used for customer support or service inquiries. It ensures that customers have a direct line to the support team, facilitating timely assistance.
2. “hr@organization.org”. As the name suggests, this address is designated for human resources. Potential job applicants, current employees with HR-related queries, or external entities needing to liaise with HR would use this address.
3. “billing@serviceprovider.com”. This would be the go-to address for queries related to invoicing, payments, or any financial transactions. It ensures that financial matters are directed to the appropriate department, ensuring accuracy and promptness in responses.
4. “sales@brand.com”. Used for sales inquiries, potential clients or partners interested in a company’s products or services would reach out through this address. It ensures that sales leads are captured efficiently and addressed by the right team.
More examples for you:
- marketing@company.com
- techsupport@softwarefirm.com
- procurement@manufacturer.net
- editorial@magazine.org
- feedback@serviceprovider.com
- legal@corporation.com
- investorrelations@firm.com
- events@association.org
- research@institute.edu
- admissions@university.edu
Benefits and drawbacks of role-based email addresses
Advantages of Role-Based Email Addresses
Role-based email addresses are common in businesses today, and for good reasons. These emails are tied to specific roles or departments, like “hr@company.com” or “finance@organization.org,” and offer several benefits.
Direct Communication. Role-based addresses make it easy for people to contact the right department. This removes confusion that might come with using a general email, so messages go straight to the right place.
Clear Responsibility. When an email is linked to a role, there’s a clear point of contact. The person or team assigned to that role knows they’re responsible for handling messages that come to that address. This helps create accountability.
Efficient Workflow. Because emails go directly to the right team, there’s less need for forwarding or redirecting. This saves time and makes sure responses are quicker, which improves satisfaction for everyone involved.
Disadvantages of Role-Based Email Addresses
Missed Emails. When people change roles or leave the company, important emails can get missed. New team members may not know about ongoing conversations or may overlook older emails. This can lead to misunderstandings or missed opportunities.
Complex Tracking. As a company grows, the number of role-based emails can increase. This makes it harder to keep track of each address and ensure they’re checked regularly. It can also be challenging to set up the right forwarding rules and train staff on which address to use. There’s also the extra work of informing external contacts if any addresses change.
Warming Up With Warmy.io in the Context of Email Addresses
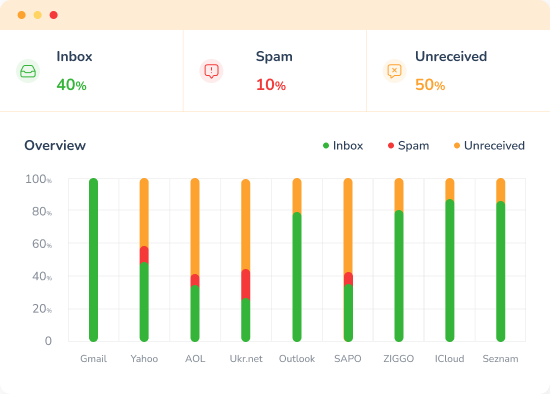
The reliability and deliverability of your emails are crucial, and tools like Warmy.io can be invaluable in this regard.
Warmy.io is an email warm-up service designed to improve the deliverability of your emails, ensuring they land in the recipient’s primary inbox rather than the spam folder.
Warmy.io and Its Relevance About Generic vs. Role-Based Email Addresses
- Enhanced Deliverability for Role-Based Addresses. Role-based email addresses, given their specificity, often receive tons of emails. Warmy.io ensures that important emails sent to these addresses from new contacts don’t end up in spam, maintaining effective communication.
- Trustworthiness for Generic Addresses. Generic email addresses, being a catch-all, are often targeted by spammers. Using the free email deliverability test, including SPF and DMARC generator, can help businesses ensure that their outgoing emails from these generic addresses maintain a high reputation, making them more credible in the eyes of email service providers.
- Consistent Communication. Whether you’re using a generic or role-based email address, having consistent communication is vital for business success. Warmy.io ensures that email messages reach the intended recipients fostering better relationships and clearer communication.
Incorporating tools like Warmy.io in your email strategy, irrespective of whether you’re leaning towards generic or role-based email addresses, can significantly enhance your email communication’s effectiveness and reliability.
It’s an added layer of assurance in the intricate dance of digital correspondence
Start your journey with Warmy.io today and experience the difference with a 7-day free trial!
Generic or Role-Based?
Choosing between generic and role-based email addresses is not merely a matter of taste; it’s strategically significant, as it affects efficiency, brand perception and engagement with audiences. Generic email addresses cover your bases and make management easy, but they can be less targeted and effective than role-based ones.
Role-based addresses ensure direct and relevant communication but come with challenges in management and potential communication gaps due to role transitions. Ultimately, businesses must weigh these benefits and drawbacks in the context of their unique operational needs and communication goals.
Using Warmy.io and its email warmup services can help either way. Maintaining a highly reputable email system can present your business as credible and highly trustworthy.
📜 Related articles:
FAQ
1. How does a role-based email address differ from a generic one?
A role-based email address is tied to a specific job function or department within an organization, like "hr@company.com" or "sales@brand.com", ensuring direct communication with that particular role or department.
2. Are there any challenges associated with role-based email addresses?
Yes, potential challenges include communication gaps when roles change and the complexity of managing multiple role-specific addresses.
3. Which type of email address offers a more personal touch in communication?
Role-based email addresses tend to offer a more personal touch as they direct the sender to a specific department or function, whereas generic email addresses might seem more impersonal.
4. How can businesses manage the potential drawbacks of generic email addresses?
Implementing effective email management systems, setting clear response time targets, and regularly reviewing the inbox can help mitigate the drawbacks of generic email addresses.
5. Is one type of email address better than the other?
Neither type is universally better. The choice between generic and role-based email addresses depends on the specific needs, communication strategy, and structure of the organization.
6. Can a business use both generic and role-based email addresses?
Absolutely. Many businesses use a combination of both to cater to different communication needs. For instance, general inquiries might go to a generic address, while specific departmental concerns are directed to role-based addresses.
7. How can businesses ensure timely responses with role-based email addresses?
Regular training, setting up automated acknowledgment emails, and integrating tools to manage and monitor email traffic can help ensure timely responses.
8. Are there security concerns associated with either type of email address?
Both types of email addresses can be targeted for phishing or spam. It's essential for businesses to have robust security measures in place, irrespective of the email address type.











