Ensuring that your emails land in recipients’ inboxes is getting more and more complex.
Sending limits and anti-spam measures are being imposed by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and Email Service Providers (ESPs) to prevent unwanted emails from reaching users. As a result, errors sometimes occur for even legitimate senders—affecting their email campaigns.
The SMTP Error 421 4.7.26, for instance, is a widely supported code from many email servers when a rate limit has been reached and messages are temporarily rejected. This happens most commonly when the sender sends many emails to many recipients in a short period of time, which in turn activates throttling mechanisms designed to prevent spam.
Nevertheless, if not managed properly, it can have a massive impact on email deliverability, campaign performance, and sender reputation.
What is SMTP Error 421 4.7.26 and what does it mean?
SMTP Error 421 4.7.26. indicates that the recipient’s email server has temporarily refused messages because the sender has hit sending rate limits.
So actually SMTP 421 is a temporary error code, which indicates the server has rejected the message but the sender can try later. Whereas permanent errors (5xx errors) indicate that the email cannot be delivered, 421 errors do not—they just mean that the server cannot take a message at this moment or that it is applying restrictions.
A typical 421 error message may look like this:
CopyEdit
421 4.7.26 – Email rate limit exceeded, try again later.
Each part of the code has a specific meaning:
- “421”: Indicates a temporary SMTP failure.
- “4.7.26”: This sub-status code specifies that the email rate limit has been exceeded.
- “Email rate limit exceeded, try again later”: The descriptive message from the recipient server explaining the reason for the rejection.
The main distinction of 421 4.7.26 is that it specifically relates to sending rate limits, rather than server unavailability or connectivity issues
Why do email servers impose sending rate limits?
Sending rate limits are applied by most email service providers (ESPs) and internet service providers (ISPs) to:
- Prevent spam: Email providers impose rate limits on bulk senders to prevent spam against users.
- Maintain server performance: The large amount of email traffic that spam takes up can overload email servers and cause them to slow down, or even go down completely.
- Preserve sender reputation: If a certain email sender suddenly sends a huge volume of emails, it may be tagged as suspicious activity.
- Comply with anti-spam regulations: Many providers apply rate limits to prevent spammy activity to better comply with rules such as CAN-SPAM, GDPR, and CASL.
Common causes of SMTP Error 421 4.7.26
Sending too many emails in a short time
To prevent abuse, ESPs and ISPs have predefined rate limits that dictate how many emails can be sent per second, minute, or hour. These thresholds vary depending on the provider and the sender’s reputation. So if a sender suddenly ramps up their email volume—such as launching a mass marketing campaign—email servers may interpret this as suspicious behavior and temporarily reject messages. This can disrupt email workflows and cause delays in campaign execution.
When too many emails are sent in rapid succession, the server enforces a temporary throttling mechanism by rejecting additional emails with the 421 4.7.26 error. The server may eventually allow sending to resume, but persistent rate limit violations can lead to more serious deliverability issues.
Exceeding the daily sending limits
Most email providers set daily sending caps to prevent misuse and protect their infrastructure. For example:
- Google Workspace: 2,000 messages per day for standard accounts and 500 emails per day for free Gmail users.
- Microsoft 365 (Outlook): 10,000 recipients per day, but individual mailbox restrictions are often lower.
Once you have reached these limits, the provider may suspend your ability to send emails temporarily or delay sending attempts until your next reset time. For businesses using email for sales, marketing or transactional messaging, reaching these thresholds can lead to widespread disruptions.
Bulk senders—especially for large-scale cold outreach or email marketing—are especially prone to this issue. Sending concentrated high-volume bursts of emails can trigger rate limiting intentionally to control the flow of emails hitting the recipient’s inbox, causing email delivery delays or even dropping emails altogether.
🔖 Related Reading: How to Send Bulk Emails Without Spamming
Poor IP and domain reputation
Email providers assess sender reputation to determine whether an email should be delivered, delayed, or rejected. Rate limits (including SMTP Error 421 4.7.26) are more likely to be imposed on senders whose IP address or domain has a poor reputation.
- Providers use metrics such as historical email performance, interaction rates, spam complaints, and bounce rates to give you a reputation score. Senders with a low reputation receive stricter rate limits than senders with a good reputation.
- If a sender’s domain or IP address is on a blacklist (Spamhaus, SURBL, UCEPROTECT, etc.), their emails may get blocked or severely throttled. Spam filters also look at the content of the email, its metadata, and past behavior to decide if a message should be accepted or rejected.
- Other factors include past spam complaints, poor engagement rates, sending from very recently registered domains, or shared IPs with some other senders of doubtful reputation. Once a sender gets flagged, they can expect to have consistent rate-limiting issues until their reputation improves.
Email server configuration issues
Misconfigured email authentication records may lead recipient mail servers to scrutinize the message more rigorously, raising the odds of rate limit hits.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): A missing or misconfigured SPF record can make it difficult for recipient servers to determine if the sender is allowed to send emails on behalf of their domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): DKIM ensures that emails are properly signed and validated. Without DKIM, those messages can attract suspicion, ending up either throttled or outright rejected.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): DMARC is an email authentication protocol that integrates with SPF and DKIM to implement more stringent authentication policies. However, overly strict or misconfigured DMARC policies for a sender can result in mail deliverability issues and an increase in bounce rate.
- Improper SMTP relay settings: Some businesses use third-party SMTP relays to send emails, but misconfigured settings (such as incorrect relay authentication or missing return paths) can cause throttling and rejections.
🔖 Related Reading: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Boosting Email Security and Deliverability
High bounce or complaint rates
If a sender experiences high bounce rates or excessive spam complaints, they are more likely to encounter SMTP 421 4.7.26 errors.
- If a high percent of the emails bounce, the email providers can recognize it as poor email hygiene and temporarily limit mail sending.
- If recipients hit the spam button, email providers may consider the sender to be a potential spammer and clamp down on future emails.
- Email services track recipient actions like opens, replies, and clicks. Emails that receive very little engagement, or worse generate multiple negative interactions (spam reports or mass deletions without opening) have a higher chance of facing rate limits.
- It is worth noting that frequent hard bounces (from invalid or non-existent addresses) indicate bad list hygiene, which is another blow to your sender reputation.
How to fix SMTP Error 421 4.7.26
Here are practical solutions you can implement to resolve and prevent this error from occurring, ensuring seamless email delivery and maintaining a strong sender reputation.
Reduce sending volume
The fastest means of alleviating SMTP 421 4.7.26 is to limit the number of emails sent over a short period. Sending thresholds are enforced by mail servers, so they must be respected.
- Tweak sending limits to stay within thresholds: Verify respective email providers’ sending policies (Google Workspace, Outlook, SMTP providers) and configure your sending tool accordingly.
- Implementing gradual ramp-up strategies: Rather than targeting your whole list and with large email blasts right away, you should start from small batches and grow the amount systematically. Most email providers get suspicious when they see a sudden volume increase, so warming up a new domain or mailbox is essential.
Checking and optimizing authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Proper email authentication is essential to gaining trust with email providers. Misconfigured DNS records can lead to deliverability problems and increase the chances of emails being throttled.
How to verify DNS records by using tools like:
- MxToolbox (SPF, DKIM, DMARC checks)
- Google Postmaster Tools (Reputation & authentication monitoring)
- Warmy.io’s Email Health Check (Comprehensive email diagnostics)
Regularly check if SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are set up correctly. Ensure the following:
- SPF record authorizes all your email-sending services.
- DKIM signature is enabled for authentication.
- DMARC policy is properly aligned (avoid “reject” policies until fully tested).
Without proper email authentication, ISPs may treat your emails as suspicious, enforcing stricter rate limits and spam filtering.
Improve sender reputation
Sender reputation is one of the biggest factors influencing email deliverability. A low reputation can lead to SMTP 421 4.7.26 errors—yes, even if you stay within sending limits. Meanwhile, a high sender reputation leads to higher sending limits and fewer rate-limit issues.
- Use an email verification tool to regularly clean old, invalid, or risky email addresses from your list. This reduces bounce rates, which are a key factor in email throttling.
- Best practices for avoiding spam complaints:
- Send only to engaged recipients who expect to receive your emails.
- Avoid spammy words and misleading subject lines that could trigger complaints.
- Make unsubscribe links clear to prevent recipients from marking emails as spam.
Set up throttling in email campaigns
- Using SMTP relay providers and email queue management: If sending large volumes of emails, consider using:
- Transactional SMTP services (like Amazon SES, Mailgun, or SendGrid) that handle high-volume sending.
- Load-balanced SMTP relays to distribute sending volume across multiple servers.
- Best practices for spaced-out sending:
- Break large campaigns into smaller batches spread over several hours/days.
- Use time-based sending rules (e.g., max 200 emails per hour) to avoid triggering ISP rate limits.
- Monitor real-time bounce and spam reports to adjust sending rates dynamically.
🔖 Related Reading: Maximizing Email Deliverability: Grouped vs. Randomized Sending
Contact your email provider
If you frequently hit sending limits, you may need to request higher limits from your email provider.
- Some providers, such as Google Workspace and Microsoft 365, allow business accounts to request higher sending quotas after proving legitimate email use.
- If using SMTP providers (Amazon SES, SendGrid, Mailgun), contact customer support to explore upgraded plans or dedicated IPs for increased sending capacity.
Additional tips to prevent rate limit issues
- Understand your provider’s limits. Each provider enforces different sending limits so make sure to review their policies to stay compliant.
- Segment and Personalize email campaigns. Sending targeted emails to smaller, well-defined audience segments reduces bounce rates and improves engagement, lowering the risk of rate limits. Customizing emails with recipient names, company details, and relevant content encourages positive interactions, reducing spam complaints and boosting sender reputation.
- Regularly monitor deliverability metrics. Monitor open rates, bounce rates, spam complaints, and unsubscribe rates to detect potential deliverability issues before they escalate. Tools like Warmy.io’s deliverability test helps check inbox placement, identify spam triggers, and assess email health before launching large campaigns.
Avoid rate limit issues once and for all with Warmy.io—an all-in-one email deliverability tool
While SMTP errors are often unavoidable due to rate limits and email provider restrictions, proactive measures can significantly reduce their occurrence and impact. Warmy.io offers powerful tools and strategies to optimize email deliverability and prevent rate-limiting errors like SMTP 421 4.7.26.
Reliable email warmup process and advanced seed list
Warmy.io progressively increases email sending volume to help build sender credibility and ensure that ISPs recognize your emails as legitimate. Additionally, Warmy uses advanced seed lists which mimic human behavior—emails sent receive opens, replies, and clicks, reinforcing sender trust and reducing the likelihood of being throttled by mail providers. In the event that an email lands in spam, it is removed and marked as important to send positive signals for future deliverability.
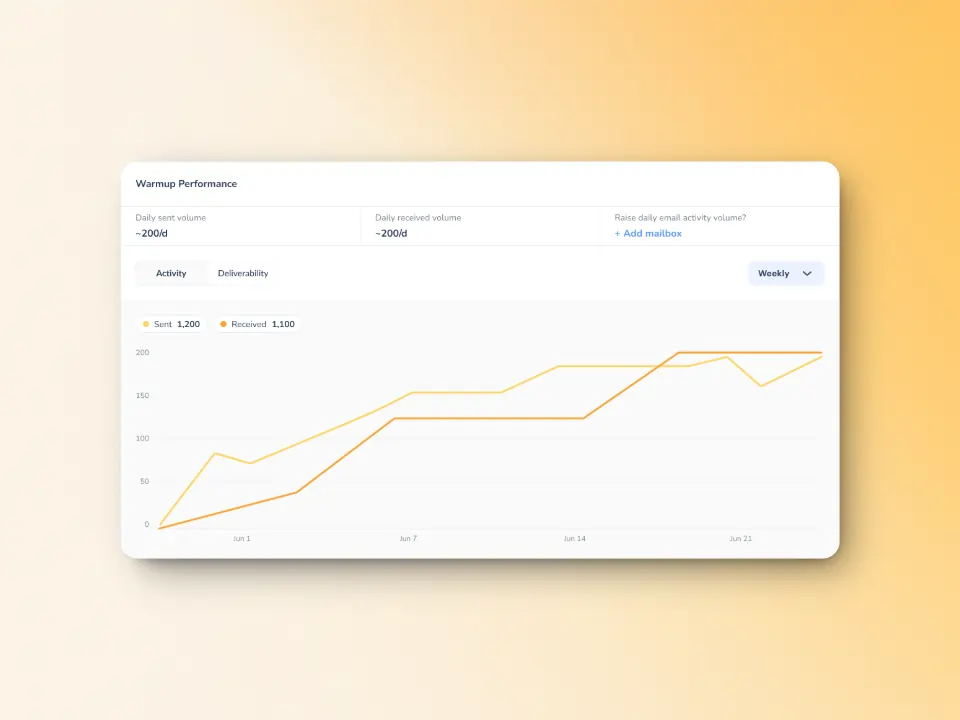
Inbox placement & email deliverability testing
Warmy.io’s email deliverability test helps users identify whether emails land in the inbox, spam, promotions, or are rejected. Users will also receive insights into how different providers (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, etc.) treat your emails so you can adjust your sending strategy accordingly.
Warmy.io also scans major spam blacklists to ensure your domain and IP remain in good standing. If an issue arises, you’ll be notified immediately to take corrective action before your emails are blocked.
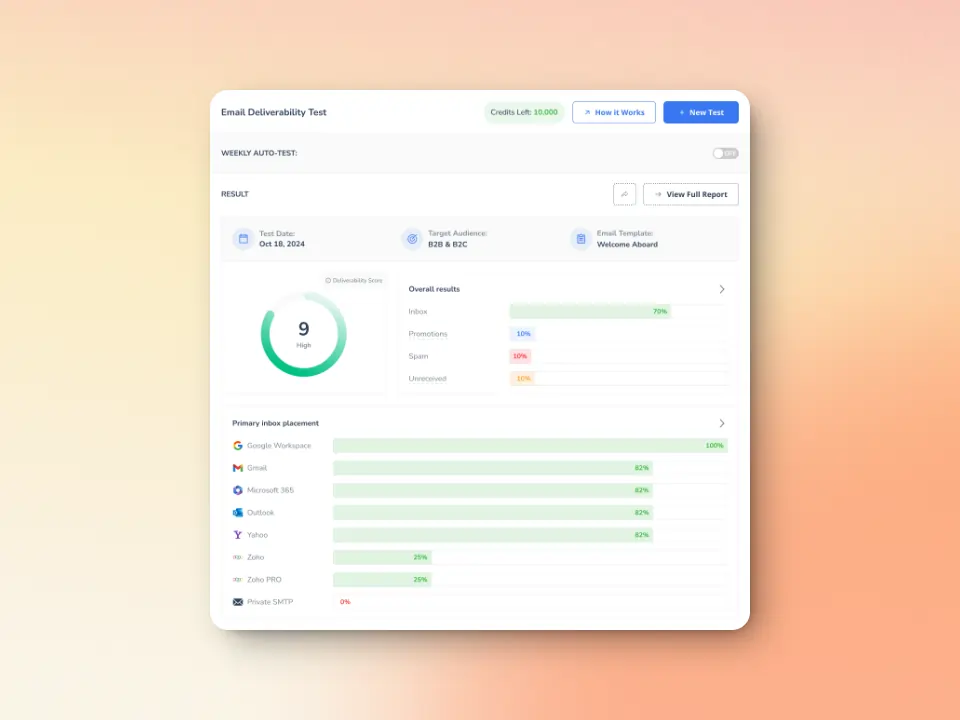
Try Warmy’s free deliverability test today.
Proper authentication verification
By ensuring proper authentication, Warmy.io helps reduce spam filtering, prevent email rejections, and improve sender reputation, all of which contribute to avoiding SMTP 421 rate-limit errors. Additionally, Warmy provides the following free tools:
- Free SPF Record Generator to help you generate SPF records for authentication of your email servers
- Free DMARC Record Generator to create DMARC policies for domain protection against spoofing and cyberattacks
Data-driven insights on domain health
Warmy’s Domain Health Hub enables users to track the performance of the domain as a whole by providing a deliverability rating based on Inbox Placement, DNS Authentication, and Google Postmaster Data. The dashboard also tracks spam rates, inbox placement, and sender reputation trends.
The domain health hub includes comprehensive DNS Status Checks to easily validate SPF, DKIM, DMARC, rDNS, MX, and A records for stronger authentication & security.
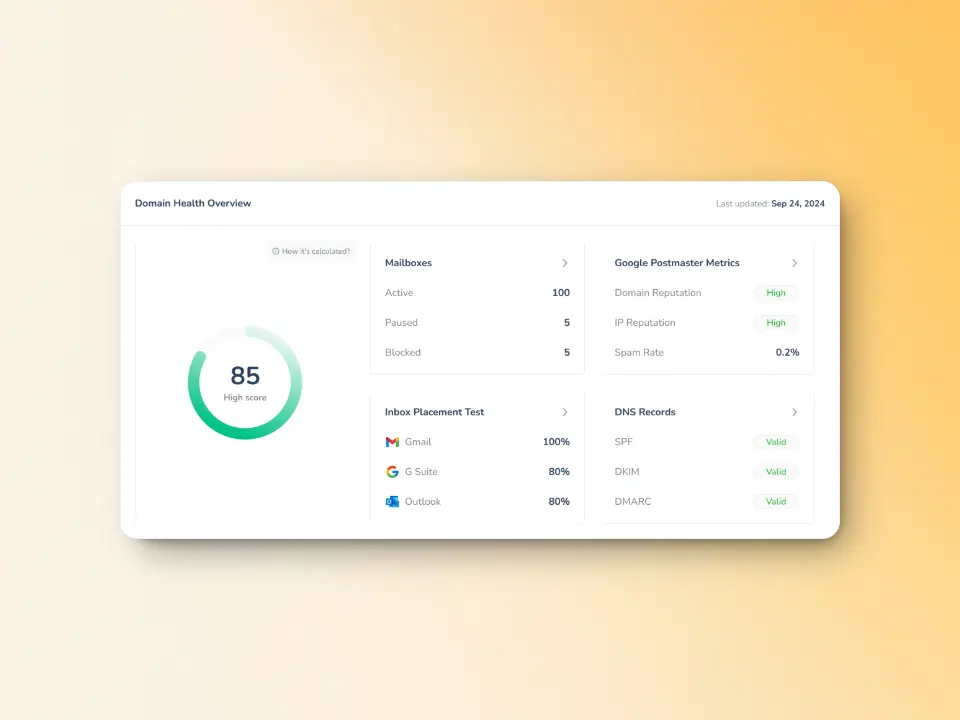
potential SMTP errors through continuous performance tracking and AI-driven recommendations.
Take control of your email deliverability with Warmy.io
Preventing SMTP errors like 421 4.7.26 is not just about fixing rate limits when they happen—it’s about proactively maintaining a strong sender reputation, ensuring proper authentication, and optimizing email warm-up strategies.
Don’t let SMTP errors disrupt your email marketing or sales outreach. Sign up for a free trial today and start sending with confidence!











